How to use¶
Here described is how you use a given input, which initializes an EBM, to run a simulation with it.
We will write a small python script, which will do this in a few steps. As it is easier to visualize the output in a plot and modify it, I recommend to perform this steps in a jupyter notebook.
Skip detailed description
Step 0: Import packages¶
Before you can use any module of this package you have to import the core modules:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from lowEBMs.Packages.Configuration import importer
from lowEBMs.Packages.Variables import variable_importer
from lowEBMs.Packages.RK4 import rk4alg
from lowEBMs.Packages.ModelEquation import model_equation
First Step: Import model configuration¶
The way this project is built up enables to take any physical function implemented and merge them to formulate the desired EBM. The configuration has to be given manually and is stored in a configuration.ini file. Details on how to create and structure .ini files is given in input.
Important
The configuration.ini file will provide the physical sense of the EBM!
For now you can simply use the EBM0D_simple_config.ini file which imports a 0D EBM with a model run over 10 year and a stepsize of integration of 1 day. A demonstration on how to reproduce this .ini file is given in Example Input 0D-EBM.
To import the information from this file into the program use importer():
configuration=importer('EBM0D_simple_config.ini')
Note
In case you work in another directory than the installation directory of the project or get the error ‘File not found’, add the additional argument path: importer('filename',path='path/to/your/file'). The path can be a relative or full path to where your configuration.ini is located.
configuration is an dictionary which contains all required input parameters. To seperate them for a clearer structure you can use:
eq=configuration['eqparam']
rk=configuration['rk4input']
fun=configuration['funccomp']
ini=configuration['initials']
Those are four dictionaries which contain the information needed for the base equation, the runge-kutta algorithm, the functions used and the initial conditions.
Second Step: Import variables¶
As next step the information from the configuration has to be imported into the programs variablespace. To do so use variable_importer():
variable_importer(configuration)
Third Step: Start the simulation¶
Now we are ready to run the algorithm with rk4alg(). It requires the model_equation and the dictionaries we seperated before (maintain the order):
outputdata=rk4alg(model_equation,eq,rk,fun)
Depending on your settings the algorithm will need some time until it prints Finished!.
Final Step: Evaluating the output¶
The function rk4alg return three arrays, the Time, zonal mean temperature (ZMT) and global mean temperature (GMT). Other variables of interest, for example the grid specifications, can be accessed by importing the variables variablespace and additional constants by importing the constants class:
from lowEBMs.Packages.Variables import Vars
import lowEBMs.Packages.Constants as const
and then return the desired variables by their specified name, for example:
latitudinal_grid=Vars.Lat
For detailed information about output variables see section output.
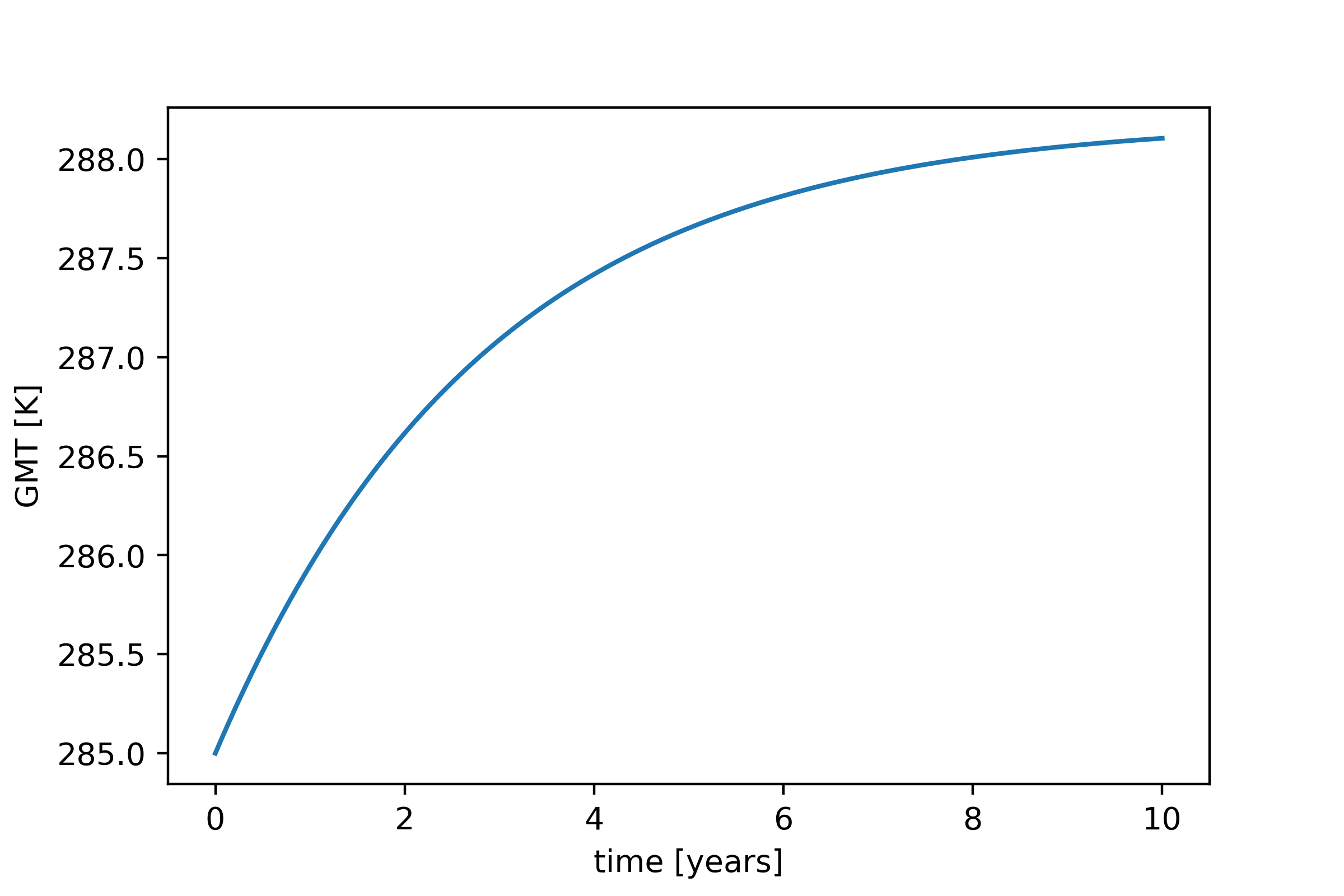
You can plot the global temperature over time with (with time conversion):
plt.plot(Time/const.time_sec_year,GMT)
plt.xlabel('time [years]')
plt.ylabel('GMT [K]')
and you get something like this (for the simple 0D EBM):
Putting it together¶
The summary of what you need to get the model running. Import packages:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from lowEBMs.Packages.Configuration import importer
from lowEBMs.Packages.Variables import variable_importer
from lowEBMs.Packages.RK4 import rk4alg
from lowEBMs.Packages.ModelEquation import model_equation
and run the specific modules:
configuration=importer('EBM0D_simple_config.ini')
eq=configuration['eqparam']
rk=configuration['rk4input']
fun=configuration['funccomp']
variable_importer(configuration)
Time,ZMT,GMT=rk4alg(model_equation,eq,rk,fun)
This demonstration also exists as a jupyter notebook in the ‘Tutorials/’ directive of this project (EBM0D_simple.ipynb).